[Avg. reading time: 6 minutes]
AWS Global Infrastructure
The Primary two items are given below.
- Availability Zones
- Regions
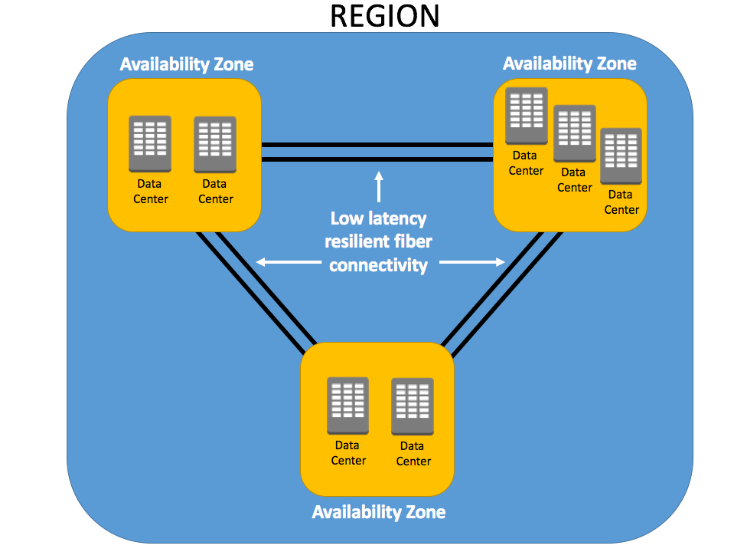
Availability Zones (AZs)
AZs are the physical data centers of AWS.
This is where the actual computing, storage, network, and database resources are hosted that we as consumers, provision within our Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs).
A common misconception is that a single availability zone equals a single data center. Multiple data centers located closely form a single availability zone.
Each AZ will have another AZ in the same geographical area. Each AZ will be isolated from others using a separate power/network like DR.
Many AWS services use low latency links between AZs to replicate data for high availability and resilience purposes.
Multiple AZs are defined as an AWS Regions. (Example: Virginia)
Regions
Every Region will act independently of the others, containing at least two Availability Zones.
Interestingly, only some AWS services are available in some regions.
- US East (N. Virginia) us-east-1
- US East (Ohio) us-east-2
- EU (Ireland) eu-west-1
- EU (Frankfurt) eu-central-1
Note: As of today, AWS is available in 38 regions and 120 AZs
Edge Location
A smaller AWS data center used by Amazon CloudFront and Lambda@Edge to cache content closer to users.
Reduces latency and improves performance for end users, especially for content delivery and inference endpoints.
A user in Singapore fetching from a U.S. model endpoint may hit an Edge Location nearby for lower latency.
Use Cases:
- DNS Resolution (Route 53)
- Content Caching